How to Play Hard Sudoku
Hard Sudoku is an advanced puzzle that requires critical thinking and strategy. Some rows, columns, or 3x3 blocks may be completely blank, leaving you to use thoughtful deduction skills to complete the grid.
Like every Sudoku game, the goal is to fill each row, column, and 3x3 block with numbers 1 through 9, avoiding duplicates in each section.
Hard Sudoku Strategies
These strategies help you observe patterns in your candidate numbers, the notes you’ve taken, to eliminate possibilities on the grid. It’s essential to methodically go over your options and erase candidates that are no longer a fit.
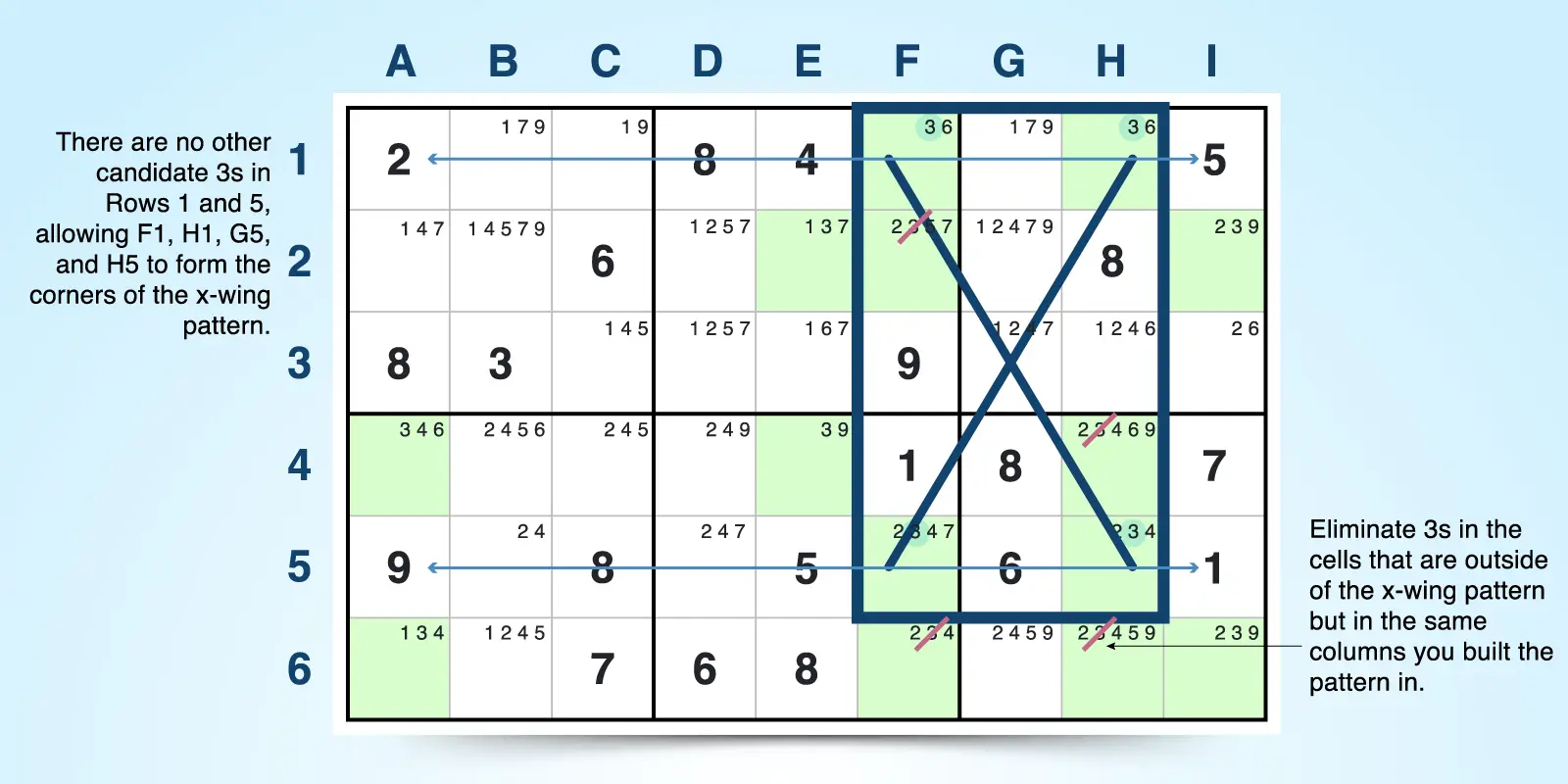
X-Wing
The X-wing strategy allows you to eliminate candidates in specific rows or columns. Look for rows or columns where the candidate appears in exactly two cells in each row or column. These four cells should align to form the four corners of a rectangle. Diagonal lines connect these corners, creating an X-shape.
Because the candidate number must occupy one of the two cells in each row and column, you can eliminate it as a candidate from any other cell in the intersecting columns and rows that fall outside the X-wing pattern.
In the example below, the 3 candidates occur twice in each row (1 and 5) as well as each column (F and H). By forming the X-wing, you can eliminate other potential 3 candidates in the intersecting columns and rows outside of the pattern.
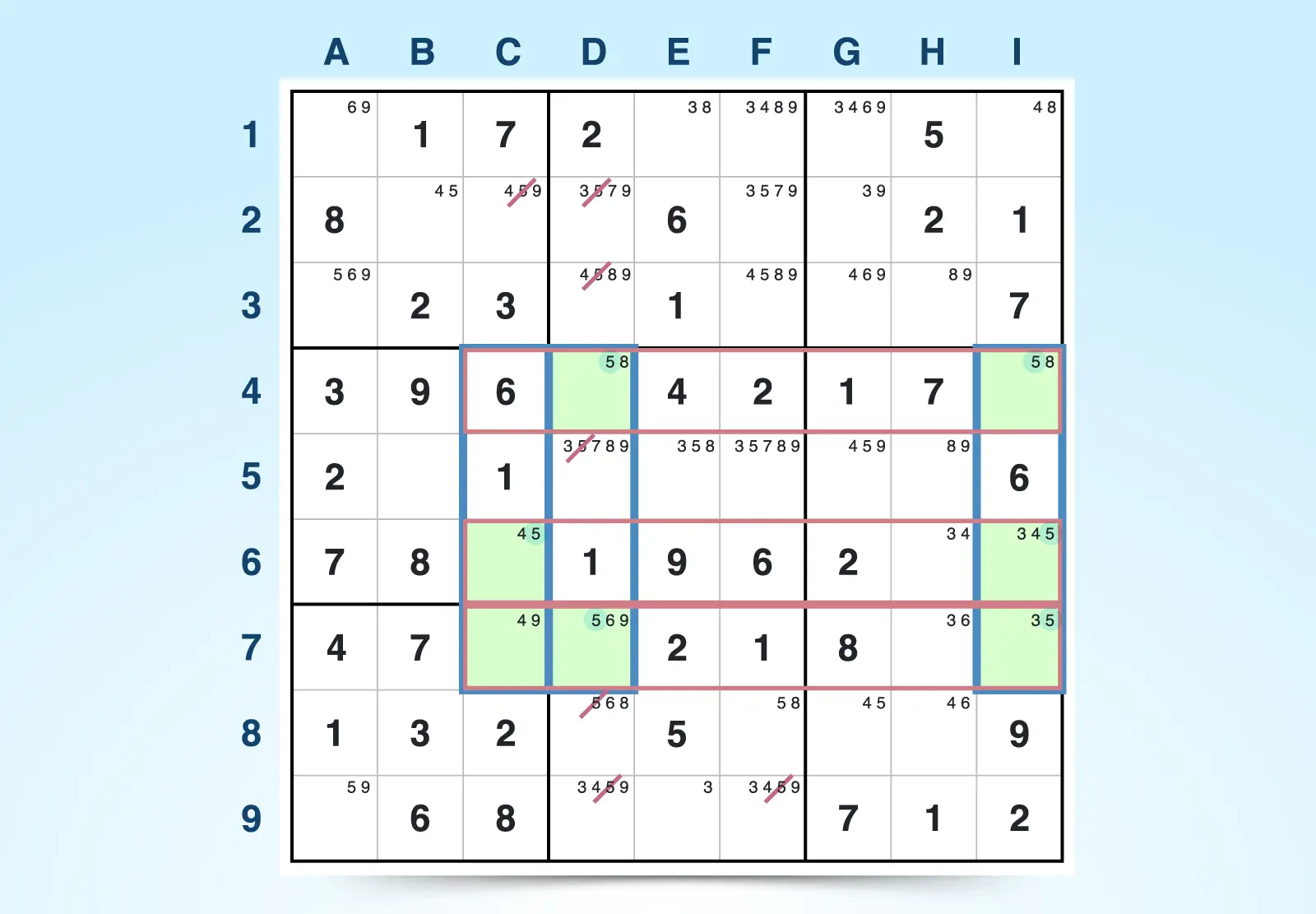
Swordfish
The Swordfish strategy is similar to the X-wing technique, but it uses three rows and three columns instead of two. To start, choose a single candidate number. It must be limited to two or three cells within each row or column. These three groups of two or three cells are called your base sets.
The base sets must also line up in the opposite direction. In the example below, 5 is the candidate number and base sets are identified in rows 4, 6, and 7. Double check that they align in the same columns — in this case columns C, D, and I.
If the set of numbers line up vertically and horizontally, you can eliminate candidate numbers that run opposite to the base sets. For example, since the base sets are rows (horizontal) you can eliminate all candidate numbers (5s) in their associated columns.
As you level up to more advanced puzzles, answers require more patience and elimination strategies. You can practice your skills with the thousands of puzzles in our archive or try techniques like coloring with our Sudoku printables.